Trading Ingredients
Ferulic acid is a phytochemical commonly found in the cell walls of plants, including grains like rice, wheat, oats, and in coffee, apples, peanuts, oranges, and vegetables such as artichokes, and eggplants. It is an organic compound belonging to the family of hydroxycinnamic acids and serves as an antioxidant in plants, protecting them against various stresses and contributing to their rigidity.
-
01 Origins and Traditional Uses

Traditionally, ferulic acid, like many plant-based compounds, was consumed through the diet. Its antioxidant properties have been recognized in traditional medicine for their potential health benefits. In various cultures, foods rich in ferulic acid have been used to promote health and prevent disease, though the explicit identification and isolation of ferulic acid for its medicinal properties are more recent developments. Traditional uses, therefore, were mostly indirect, through the consumption of ferulic acid-rich foods.
-
02 Use in Consumer Products
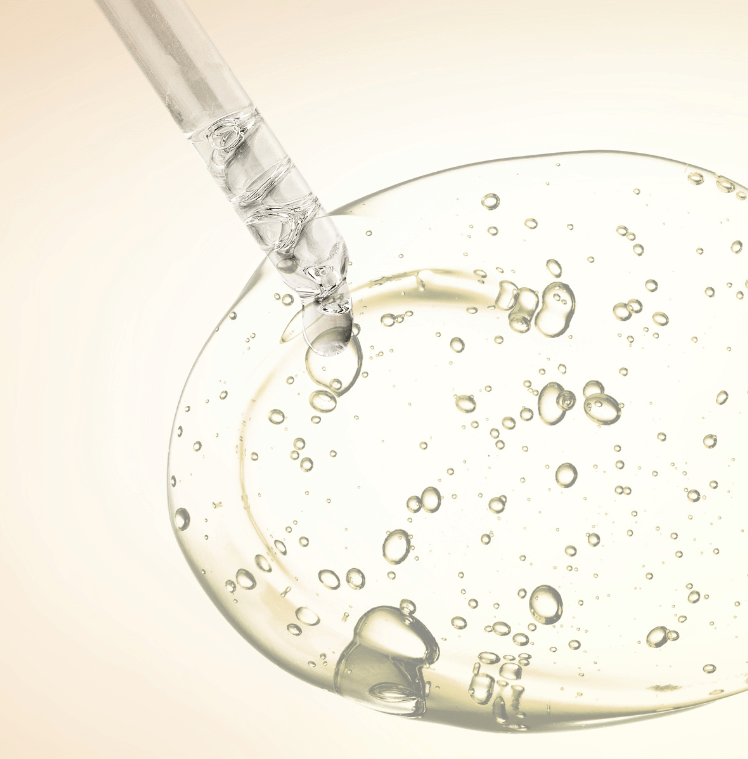
Today, ferulic acid is widely used in consumer products, primarily in the skincare and cosmetic industry, as well as in dietary supplements.
- Skincare and Cosmetics: Ferulic acid is prized for its antioxidant properties, which can help to neutralize harmful free radicals, reduce the signs of aging, and stabilize other sensitive antioxidants like vitamin C and E in cosmetic formulations. It is a common ingredient in serums, creams, and sunscreens, often touted for its ability to protect the skin from environmental damage, improve skin integrity, and enhance the efficacy of other antioxidants.
- Dietary Supplements: Due to its potential health benefits, including anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and cardioprotective effects, ferulic acid is also included in various dietary supplements. It is marketed for its ability to combat oxidative stress and support overall health.
- Food Preservation: Exploiting its antioxidant properties, ferulic acid is sometimes used in food preservation to prevent the oxidation of fats and oils, thereby extending the shelf life of food products.
In summary, ferulic acid’s origins in plant cell walls and traditional consumption through diet have evolved into a broader application across consumer products, especially in the skincare and dietary supplement industries, underpinned by regulatory frameworks that ensure its safe use.
Current Regulatory Environment
The regulatory environment for ferulic acid varies by country and depends on its intended use. In the context of dietary supplements and food additives, it is generally regarded as safe (GRAS) by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) when used within recommended guidelines. However, the specific regulatory stance can differ when it comes to its use in pharmaceuticals or as a cosmetic ingredient. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and other international regulatory bodies have similar frameworks, evaluating its safety based on its usage levels and contexts.
DISCLAIMER: This information is provided on an as-is basis for general background. Independent, verified research should be conducted on all ingredients in food, supplements, and consumer products.

2000+
Manufacturers





