Low-temp Assembly Secondary Packaging
Low-temperature assembly is a manufacturing process that involves joining components at temperatures significantly lower than traditional methods. This type of assembly is particularly important in industries where heat-sensitive components are used, such as electronics and medical devices.
The process generally involves the use of adhesives, solders, or other materials that have a lower melting point compared to standard materials. For example, instead of using traditional soldering that might require temperatures above 250 degrees Celsius, low-temp assembly might use materials that melt at 150 degrees Celsius or less. This is achieved by selecting special alloys or compounds that provide adequate bonding strength at reduced temperatures. Additionally, low-temp assembly can involve techniques like ultrasonic bonding, which uses high-frequency sound waves to create a bond without significant heat.
-
01 Low-Temp Assembly by Processing Type

- Adhesive Bonding: This method uses organic or inorganic adhesives that cure at lower temperatures. These are often used in the assembly of parts like LCD screens where high temperatures can damage sensitive liquid crystals.
- Soldering: Low-temperature solders are specially formulated alloys, often containing bismuth or indium, which melt at lower temperatures than traditional tin-lead or lead-free solders.
- Ultrasonic Welding: This process uses ultrasonic vibrations to generate heat locally at the interface of the materials to be joined, without the need for external heat sources.
- Laser Welding: Some laser welding techniques can be adjusted to operate at lower temperatures, focusing energy precisely where it’s needed to minimize thermal stress on components.
-
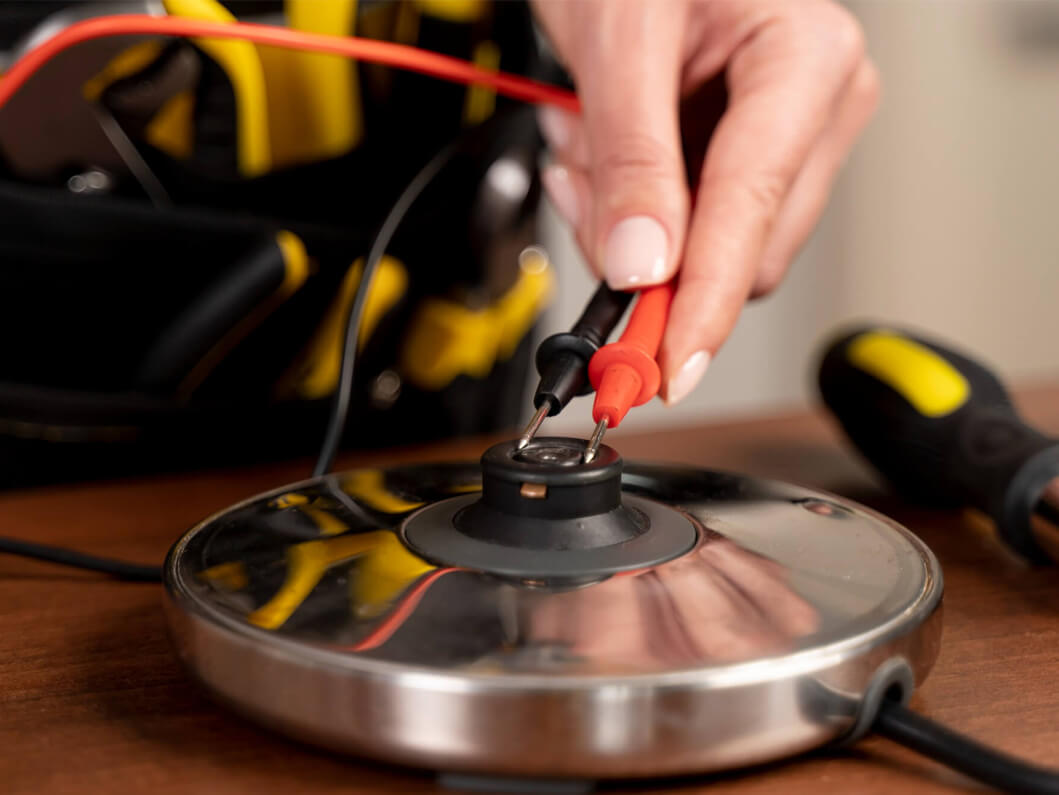
02 Benefits of Low-Temp Assembly in Processing

- Reduced Thermal Stress: Components are less likely to warp or become damaged due to high temperatures, which is crucial for delicate components.
- Energy Efficiency: Lower temperatures require less energy, which can lead to cost savings and a lower environmental impact.
- Component Compatibility: Allows for the inclusion of components that are sensitive to heat, such as certain plastics, composites, or electronic components with low melting points.
- Improved Safety: Reducing the process temperature can enhance safety by reducing the risk of burns and fires.
-
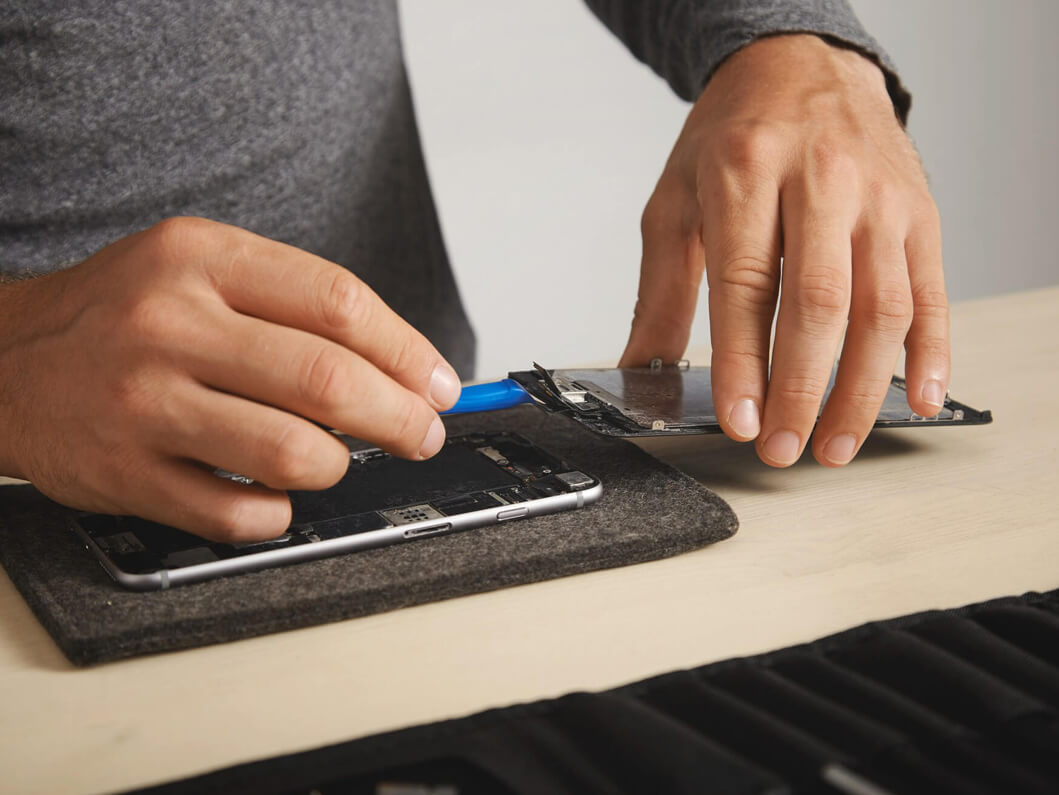
03 Examples of Low-Temp Assembly Applications
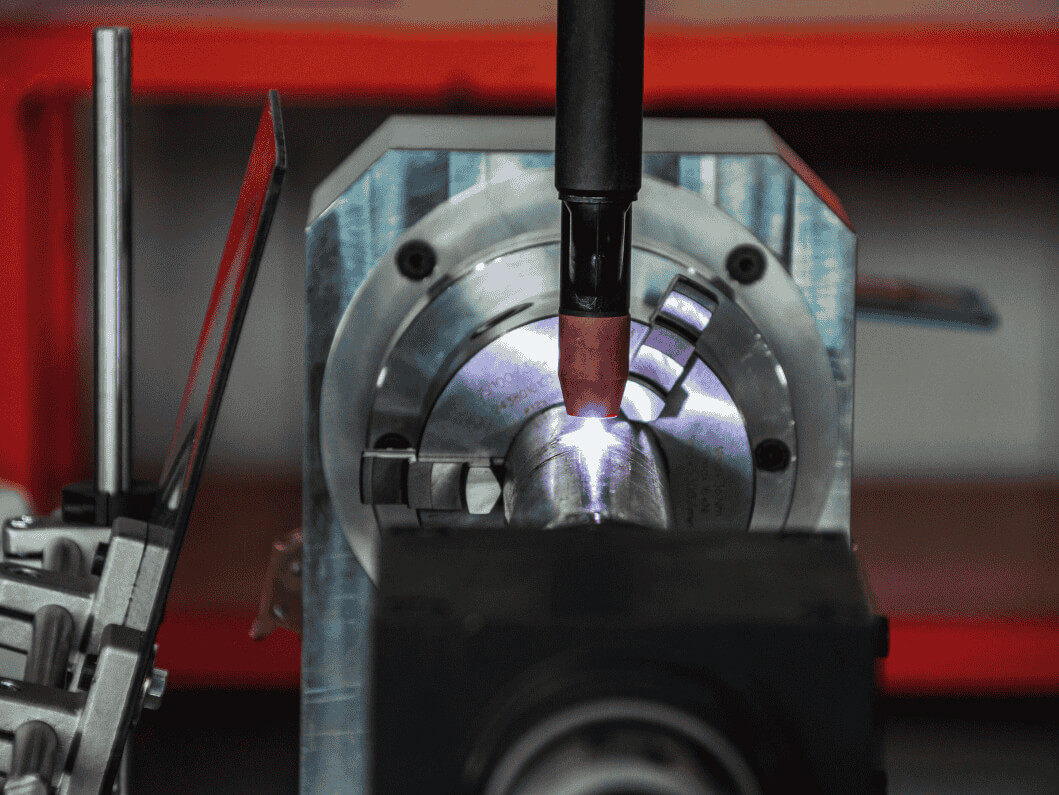
- Electronics Manufacturing: Mobile phones, laptops, and other devices that incorporate sensitive electronic components and fine circuit details often benefit from low-temp assembly to prevent damage.
- Aerospace and Automotive Industries: Components that involve mixed materials such as carbon fiber composites and lightweight alloys often use low-temp assembly to avoid damaging the structural integrity of the parts.
- Medical Devices: Many medical devices involve the use of temperature-sensitive materials that require precise and gentle assembly processes to maintain their functionality and reliability.
- Wearable Technology: The growing field of wearable technology often utilizes flexible, heat-sensitive materials that necessitate the use of low-temp assembly techniques.
- Low-temperature assembly is gaining prominence as industries continue to develop more heat-sensitive materials and as the push for energy efficiency and environmental responsibility becomes more pronounced. This method not only preserves the quality and functionality of components but also aligns with broader industry trends towards more sustainable manufacturing practices.
Your Gateway to Seamless Low-tempt Assembly Solutions
CoPack Connect can connect brands with contract manufacturers and packagers that offer relabeling services. We make it easy for businesses to find the right manufacturer for their needs and provide the tools and resources they need to manage their relabeling projects successfully.

2000+
Manufacturers





